In architecture there are two ways to be truthful: in terms of the program and in terms of construction. […] To be truthful in the construction techniques is to use the materials according to their qualities and properties. What is regarded as purely artistic issues, for example symmetry, are only secondary concerns in the face of these dominant principles.
[Viollet-Le-Duc: Entretiens sur l’architecture]
MATERIALS
materials are continuously changing as we evolve and as the time pas. We csns observe this evolution trough hystory. Materilas for primitive architecture werent the same as the medieval architecture. materials and technology are replaced by new ones. but the shapes remain alive and active, translated into new technological realities but perpetually expressed as symbols of the first materials and the primitive need to protect man
TRADITIONAL MATERIALS
STONE
Different types such as sand stone, lime stone, tuff, etc an different ways to put them(for rooftops, walls, ) such as the technique of gabion , made of dry stone masonry or Huge rough granite blocks.
EARTH
As it is everywhere, it is the most common material.
Tapia: each of the pieces of wall that are made at one time with
rammed earth and lime into a formwork.
Adobe: : sun-dried clay blocks. May contain reinforcing straw
this construction, is recovered of the surface,


BRICKS
Are fired clay blocks. Can be of different sizes and forms to put them toguether at a wall.they normaly work well at compresion. in order to reinforce bricks, iron it is used.

WOOD
Can be seen at interiors, rural houses and exteriors as well. It doesnt strtat of foundation. Rooftops are not commonly made of wood. as well as pilars or any other structural element that is made to handle big aount of cuantities of stress.However, is not forviden at all, we can see buildings completely made of wood.
MODERN MATERIALS
STEEL: a current material, allows the creation of new shapes.
CONCRETE: A very versatil material, cheep and common now a days.
GLASS: deformable in many shapes, add modernisim to buildings, natural ilumination can be profited. (The use of glass without joinery is intended to dematerialise the
enclosure)
TECHNOLOGY
ROMANESQUE ARCHITECTURE
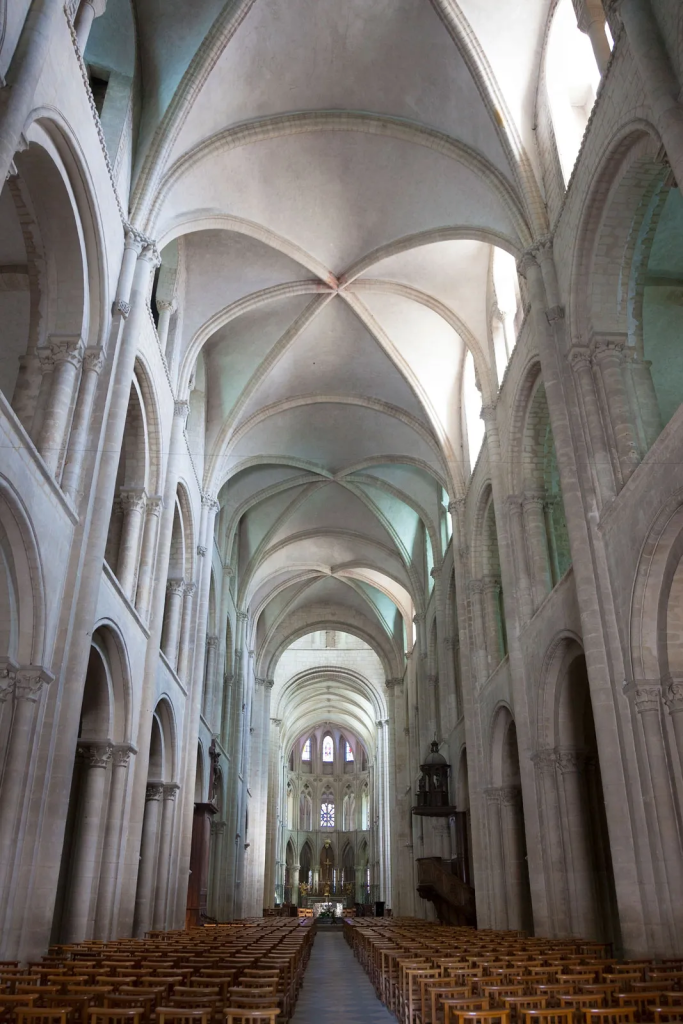

Roman construction had lot of resources, that is why they bult a lot. They used brick, stone. The basic material in Roman construction is concrete, that is arranged in a work by SHUTTERINGS in vaults and domes, and outer layers of brick, masonry or small pieces of carved stone. arch and vaults, are commonly seen in this type of architecture. (BARREL VAULT reinforced by TRANSVERSE ARCHES)
Walls are reinforced with external BUTTRESSES, with wooden TIE BEAMS at the
beginning of the vaults, with the increase of the section of the inner pillars in the
direction of the lateral thrusts.
Afterwards, BARREL VAULTS are replaced by GROIN VAULTS, which represent a new covering system that obvious the rigidity of the lateral walls to transmit directly loads to the pillars through the combined action of TRANSVERSE RIBS and FORMERETS.
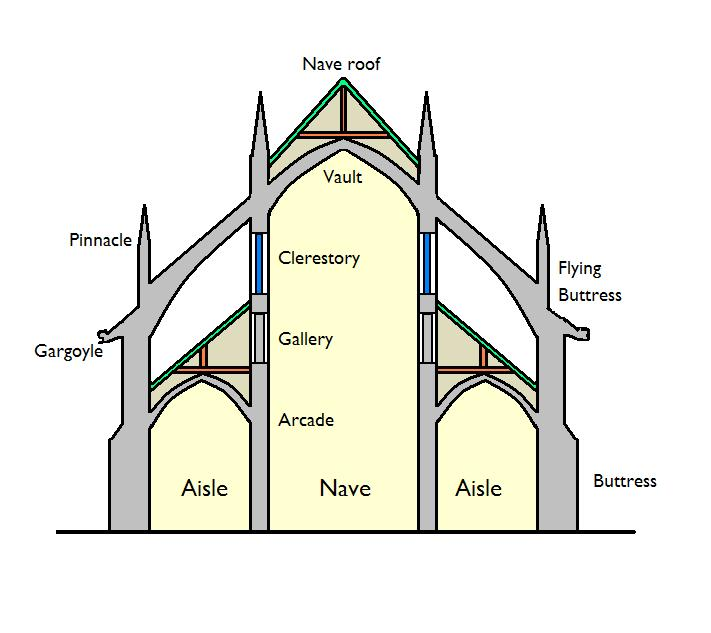
GOTHIC ARCHITECTURE
• the pointed arch
• the rib vault
• the buttress
• the flying buttress
• the pinnacles.
Compression forces opposed to traction forces
ROCK-CUT ARCHITECTURE

Monolithic temple made by carved solid natural rock. No materials are supplied. Rock-cut architecture is the creation of structures, buildings, and sculptures by excavating solid rock where it naturally occurs. Intensely laborious when using ancient tools and methods, rock-cut architecture was presumably combined with quarrying the rock for use elsewhere.
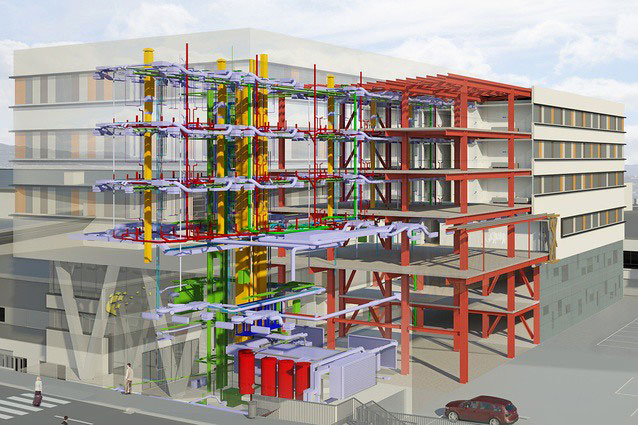
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
represents an innovation in the generation of architectural shapes.

Building Information Modelling (BIM)
also adds the collaborative management to the Project. the elements are created in 3d directly , you dreaw elements not lines.

Nowadays prefabrication, in some ways, changes the way we build or manage construction.
clt panels helps to improve resistance, are superficial materials,
grc panels are allso an other prefabricated material. they consist of a 1-2 meters pefabricated piece. not heavy as are thin,
prefabricated blocks of erath made by diferent lines of earth one above the other.an ancient technique of building that has ben modernized.



STRUCTURES
New challenges:
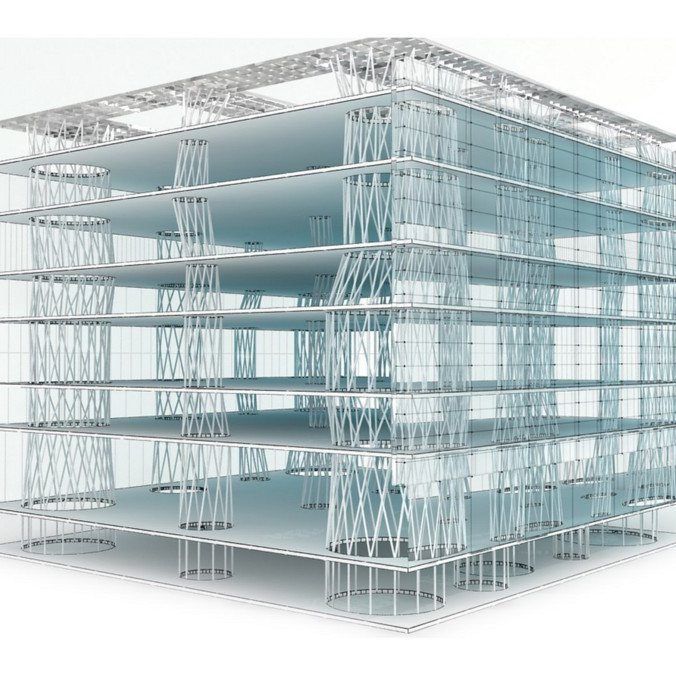
- Stability and instability as formal aesthetic principles. Extreme cantilevers
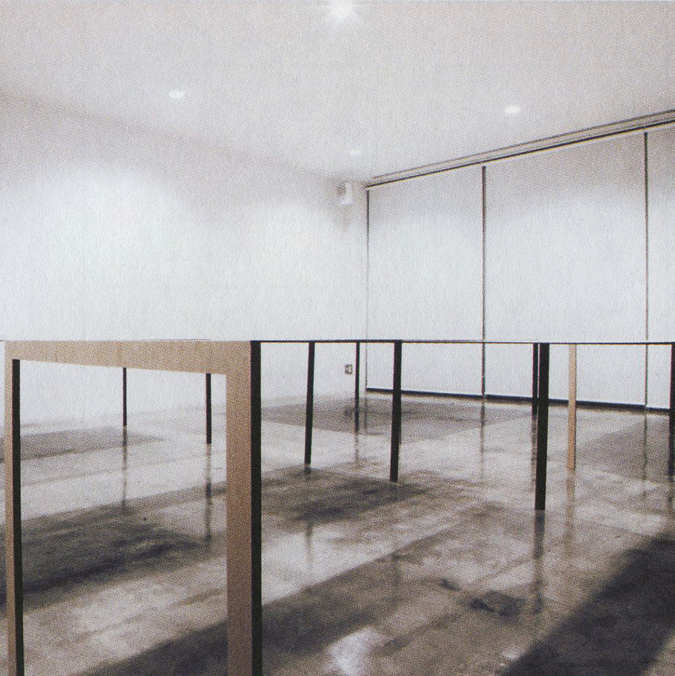
internal structures are hiden an materials create an optical effect. architects can play whith shapes in order to create stability.
- Structure dissolution with new materials and structural types. Dematerialization.
Stability and instability as formal aesthetic principles
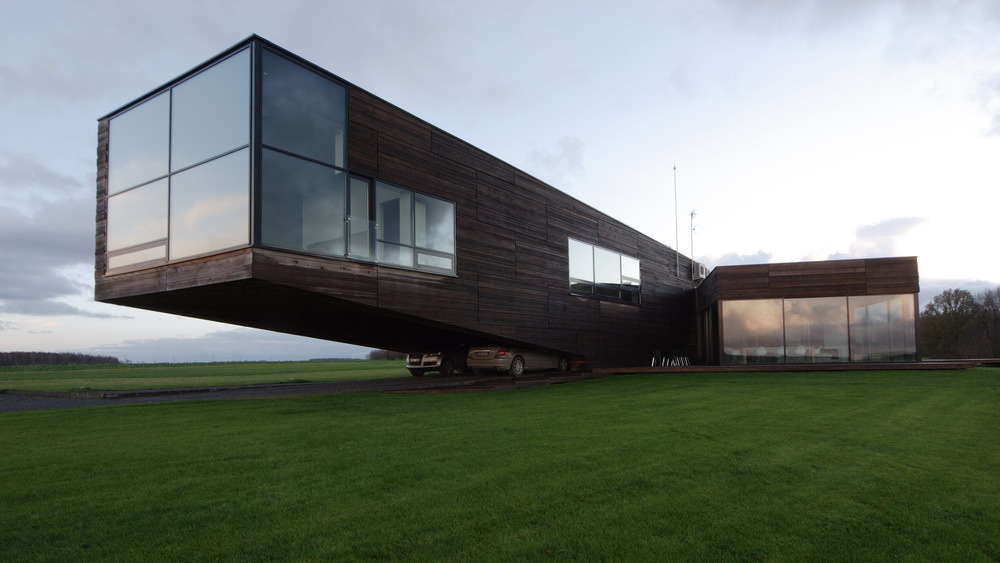
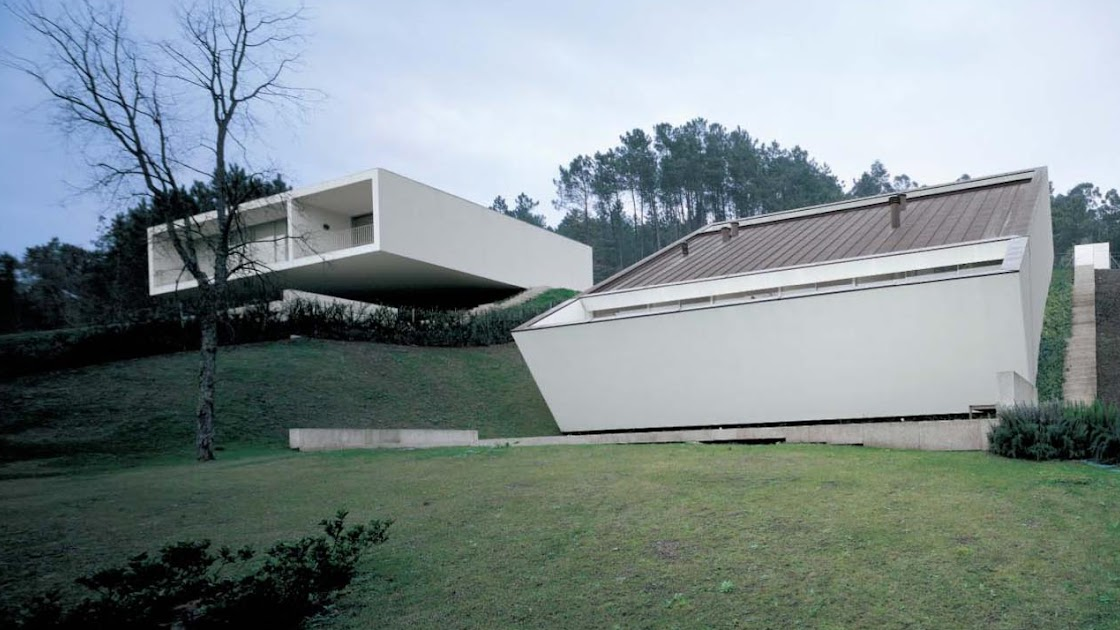



Structure dissolution with new materials and structural types
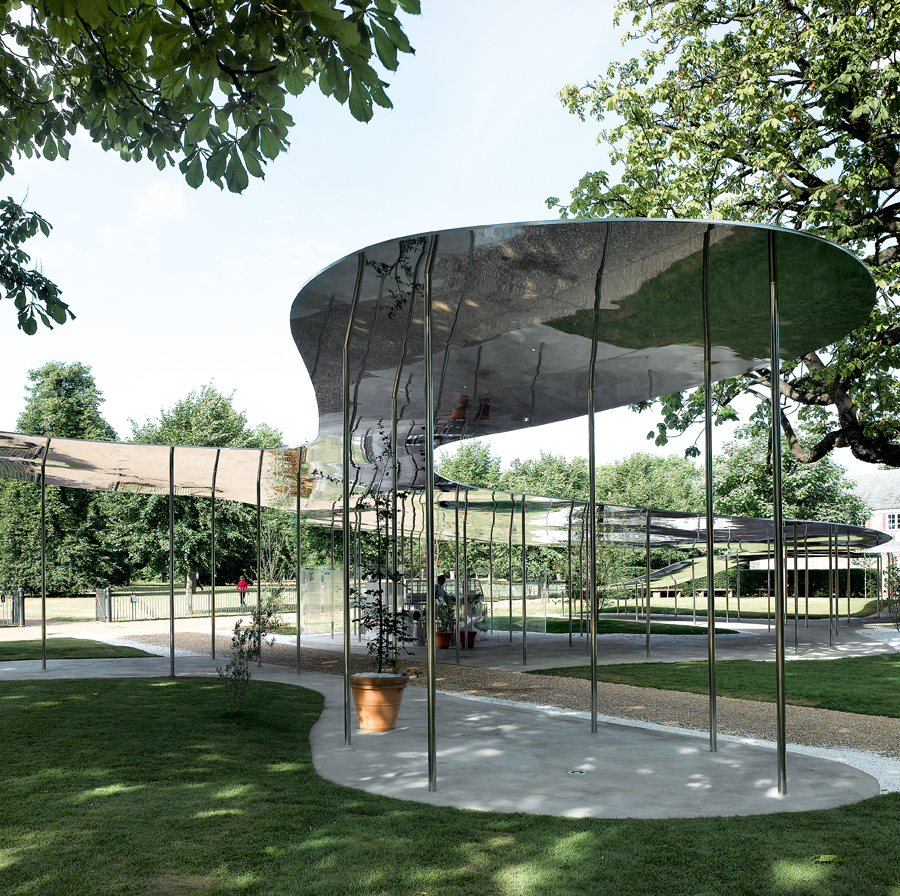


FACILITIES
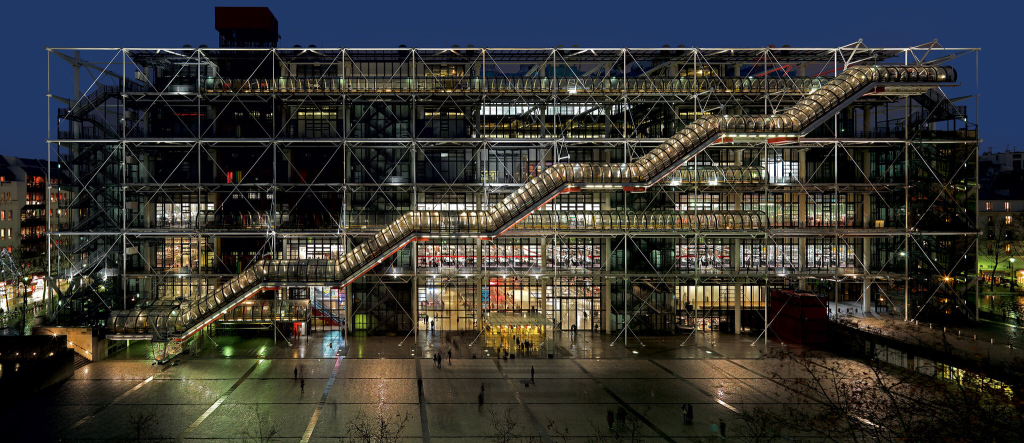
Building facilities are infrastructures formed by networks and fixed equipment that enable the supply and operation of services that allow functionality, efficiency and comfort in those for which they have been designed.
The challenge of integrating installations into architectural design is noe a real goal to architects.
Type of services:
- Energy networks:
• Electrical installation
• Gas installation
• Photovoltaic system - Hydraulic facilities
• Potable water supply
• Sanitation facility
• Fire protection systems - Climatic installations
• Ventilation
• Heating
• Air-conditioning
• Domestic hot water - Telecommunications
• Phone signal
• TV signal
• Fiberglass internet network
• Home automation
• Safety control - Medical installations
• Medical gases - Others
The challenge of integrating installations into architectural design



TO SUM UP
Materials can be divided mainly in traditional ones and modern ones. Whereas stone, brick and wood perform as a traditional material, steel, glass and concrete work as modern ones.
We have seen all along the history how materials have developed into the ones we use now a days. Materials have improve their properties till the ones today.
As we have seen today in class prefabricated buildings are highly increasing it’s popularity, this type of buildings could be the future of architecture.As well rock-cut architecture should be considered. It is quite curious, interesting and admirable.
In addition, we have seen that computer programs for designing are becoming more and more important this days for current architects. And it is a fact that aesthetics is becoming more important in buildings but always without forgetting that the building should be functional durable and safe. Also, current architects are creating projects with awesome physics, playing with balance and abstract forms. Sometimes hard to believe
I have done some research on new techniques that are being applied to the world of architecture, construction etc. and apart from the incorporation of programs such as autoocad, modern techniques are also being incorporated such as the following
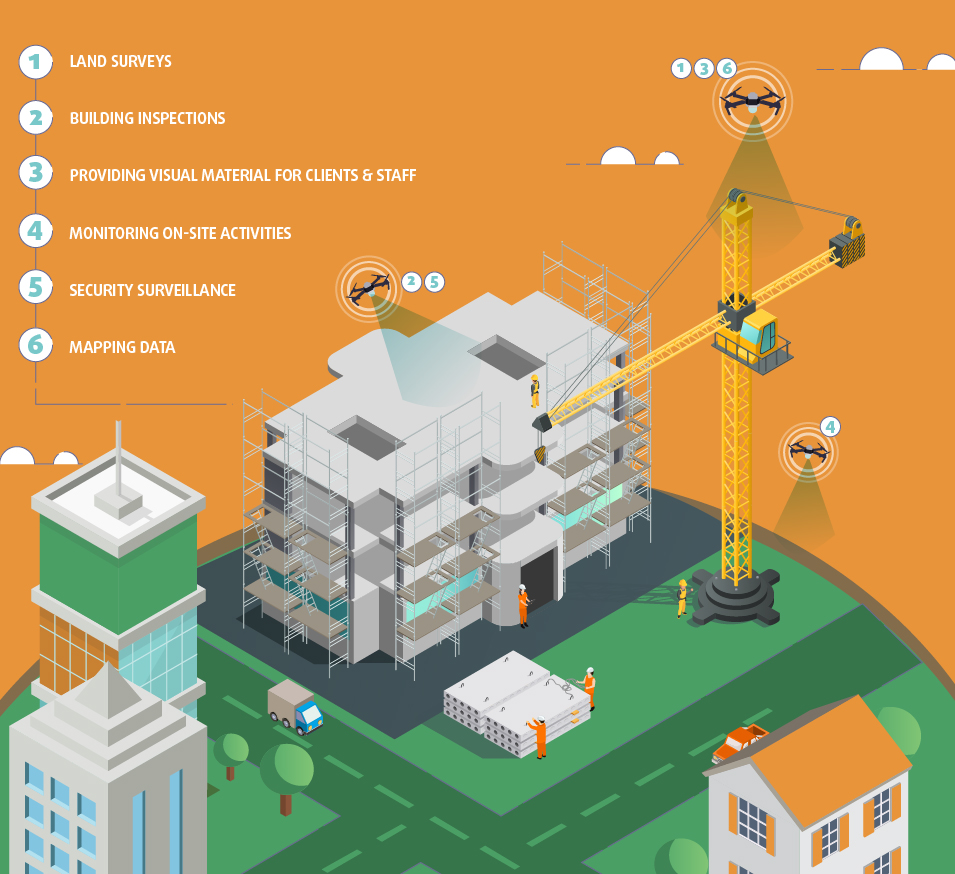
Drones applied to building
The professional use of drones has also reached architectural tasks. The recreation of the terrain with 3D computer graphics, the taking of aerial images to supervise the evolution of constructions in a precise way or the modification of structures built with state-of-the-art architectural elements are just some of the applications in this field.
Robotic Architecture
At the moment, robots are already being used to mechanize dangerous tasks (demolition, insulation projection, or those that are heavier (placement of materials, adaptation of spaces to different sizes, inspection work, cleaning…) with the aim of speeding them up and optimizing time. However, the development that robotics is undergoing leads us to believe that in the near future it will also be able to perform other tasks of greater architectural responsibility.

BIM methodology
Not only is it a revolution in itself for engineers, but architects are also experiencing its advantages in the design and maintenance phases of buildings. Keep in mind that this methodology allows immersive projects in which you can walk through the interior before they are even carried out or detect and combat errors in their planning.
